
Carburizing will help to improve the strength characteristics of various mechanical steel parts represented by automotive components.
"What is the Gas Carburizing"
Learn from the advanced management and technology of the overseas offices of the Group to demonstrate the best treatment effect.
The treatment refers to the process that adds butane, propane and other concentrated gases in endothermic metamorphic gas (RX gas) with the main components of CO, N2 and H2 in the furnace, heats the steel materials to about 900~940℃, infiltrates the carbon to material surface for carburizing and then conducts cooling quenching for hardening.
It can conduct mechanical processing on mild steel and low-carbon and low-alloy steel with good machinability, and generate a hardened and tough carburizing hardening layer on the surface after forming to an assembly shape.
In addition, the interior of the treated product is an appropriate soft tissue. As a result, the whole body can obtain high hardness while ensuring the impact strength by the high toughness, so that the wear resistance and the fatigue resistance are excellent, and the general relative "toughness and hardness" can be realized at the same time. It is widely used in various mechanical components such as automobile parts and motorcycle parts. It is one of the most popular surface heat treatment methods.
It is different from nitridation heat treatment in that it is heated above the transformation temperature of the iron and quenched and tempered by the representative method of heat treatment in the treatment process.
The company has two types of Gas Carburizing furnace, namely batch production type and mini-continuous type.
In terms of batch production furnace, a variety of conditions are supported, from a short processing time of dozens of minutes to a long processing time of more than ten hours. In addition, special Carburizing treatment systems which can be applied to Nitrocarburizing, low temperature Nitrocarburizing, anti-carburizing (using anti-carburizing agent to prevent partial carburization) and high temperature tempering are prepared.
In terms of mini-continuous furnace, the high efficiency production capacity is about 2.5 times of the batch production furnace, which supports a large number of order products under the same conditions, thus realizing the unique low cost and stable quality of the continuous furnace.
"One case of Gas Carburizing"
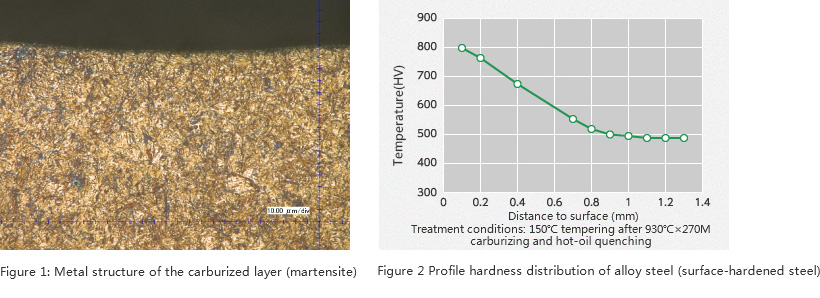
Figure 1 shows the metal structure of the carburized layer during gas carburizing quenching and tempering in alloy steel with 0.2% carbon content (surface-hardened steel).
The carburized layer forms a uniform carburizing quenching layer with about 10~15% austenite residue in the fine martensitic materials.
Figure 2 shows the profile hardness distribution of carburizing hardening layer. The surface ensures high hardness of HV800 and the depth of integral hardening layer is about 0.9mm.
The hardness of surface and the depth of hardening layer can be adjusted according to the desired heat treatment conditions.
Compared with the soft nitridation treatment, the advantage is that it is possible to form a hardened layer of high hardness, thus it is advantageous for components that require higher strength.
1. Applicable types of steel: Surface-hardened steel (SCM・SCr・SNCM and other low-carbon alloy steel)
2. A thick surface hardened layer can be obtained, and a high toughness can also be ensured in the interior.
3. The depth of hardened layer and the surface hardness can be adjusted as desired.
4. Various quenching oils can be chosen according to the internal hardness and assembly shape.
5. The surface is a smooth appearance of light gray (low temperature tempering)
6. Improve wear resistance, impact strength, fatigue resistance
"What is the Nitrocarburizing"
The possibility to improve the strength of non-alloy steels and expand the thermal treatment of steels.
Nitrocarburizing refers to a treatment process that mixes carbon and nitrogen on the steel surface 800~880℃ lower than the normal gas nitriding for quenching and hardening.
Nitrocarburizing adds NH gas in the normal gas nitriding environment and takes use of N components decomposed from NH for nitridation and carburizing.
Because nitridation can improve the quenching performance, it has the advantage that non-alloy steel such as SPCC, mild steel, which is not suitable for gas carburizing, can be treated, and the cost of the material can be greatly reduced.
In addition, since the quenching can be carried out at a temperature lower than that of the gas nitriding, the deformation and the skew caused by the heat treatment can also be reduced.
"Low temperature Nitrocarburizing"
In the process of nitrocarburizing for ultra-thin walled stamping parts, in order to meet the need of further reducing heat treatment skew, low-temperature nitrocarburizing is still being carried out. By using advanced controllable atmosphere treatment technology, the treatment temperature is reduced to about 750℃ to carry out stable ultra-shallow nitriding and greatly reduce quenching skew.
The carburizing characteristics of high-alloy steel will also be further improved.
By nitrocarburizing the alloy steel, the incomplete quenched layer in the surface part of the former gas nitriding treatment will become uniform quenched structure (martensite), so the hardness decrease of the surface layer can be restrained.
In addition, the infiltration of nitrogen has the effect of inhibiting the hardness decrease (thermal attenuation) of the components exposed to high temperature.
Nitrocarburizing treatment has been used to improve the shot blasting hardening resistance, wear resistance and other contact fatigue strengths on the contact surface of transmission parts represented by carburizing gear with alloy steel.
1. Applicable types of steel: Mild steel (SP materials, SS materials, S10C and other mild steels), surface-hardened steel (SCM・SCr・SNCM and other low-carbon alloy steels)
2. Because it can be quenched at low temperature, the quenching deformation will be reduced. (Except for surface-hardened steel)
3. Because the quenching performance can be improved by the effect of nitrogen, the carbon steel is easy to quench. It is also advantageous to quench cracks.
4. Compared with the Gas Carburizing, it can control the abnormal quenching layer on surface and generate a uniform hardening layer.
5. Improve the tempering softening resistance compared with the Gas Carburizing.

Continuous Carburizing furnace
660W×1,230L×720H(batch production furnace)
760W×615L×720H(continuous furnace)
Mechanical components centering on power parts such as engines, transmissions, differentials, etc. for transport machinery
(Gearing / shaft, CVT sheave , main decelerator, etc.)
"What is the low-temperature nitrocarburizing treatment"
Low temperature nitrocarburizing is a kind of low deformation and high hardness heat treatment for thin stamping parts. Through the establishment of advanced controllable atmosphere treatment technology which can effectively make carbon and nitrogen infiltration and diffusion at 730~820℃ below normal nitrocarburizing, Nitrocarburizing treatment is carried out at low temperature below normal 50℃. In addition, quenching can be carried out below A1 transformation temperature in Fe-C system balance diagram.
Accordingly, a shallow and high-hardness martensitic hardening layer of about 0.05~0.1mm will be formed on the surface layer.
The high and deep hardened layer can be obtained by gas or Isonite Treatment, and the deformation and size change can be greatly reduced compared with the conventional nitrocarburizing.
"One case of low-temperature Nitrocarburizing treatment"
The following introduces 1. Structure photo, 2. Chart of hardness distribution of low-temperature Nitrocarburizing.
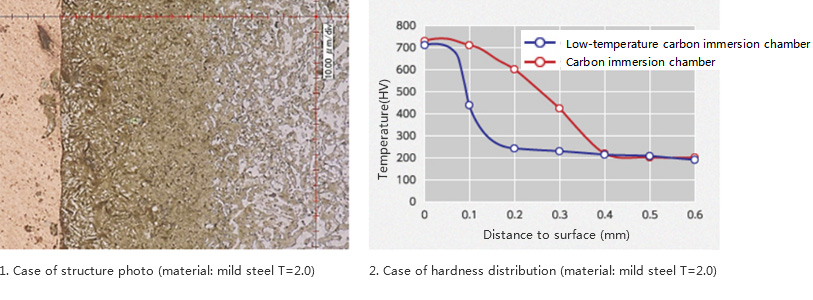
2. Case of hardness distribution (material: mild steel T=2.0)
Martensite structure will be precipitated in the surface layer, which has a high hardness. From the depth of the internal 0.1mm, ferrite structure will be maintained and transformation will not appear. Therefore, due to the height difference (sharp taper), the deformation is very small.
Compared with the conventional Nitrocarburizing, the deformation of low-temperature Nitrocarburizing can be controlled below 1/3.
"Characteristics of low-temperature Nitrocarburizing treatment"
● Reduce deformation and size [variation] by reducing thermal deformation
● Improve wear resistance, surface pressure strength and corrosion resistance
● Improve surface compression and fatigue strength
『 The above is quoted from Hamamatsu Netsushori Co., Ltd 』
